(Editorial in progress)
Baikal Tea in collaboration with Dr. Elie Klein, ND (Naturopathic Doctor, Toronto Canada).
Dr. Elie Klein, ND, had been helping people use less medication and cure causes of disease, for over 20 years. He is sharing ground-breaking concepts of health we've never heard before, and explains them scientifically.
Oxidation - the disaster of modern time
Very simply put, oxidation is a loss of electron. It is a chemical reaction that happens within each of us every day. When we lose electrons from tissue and organs, they start getting sick.
When body doesn’t have enough material to heal quickly, oxidation causes serious damage, resulting in heart issues, Alzheimer's, diabetes and other modern disease.
Excessive oxidation is very similar to the formation of rust. You might be familiar with the formation of rust–A metal wire can be flexible and strong when it’s not covered by rust. But if it becomes extensively covered by rust, if rust eats into it, then it becomes both brittle and stiff at the same time:

Oxidation involves an excessive flow of electrons in an unbalanced way. I won’t get too scientific here, this process of oxidation that causes rust, also causes the injury to the artery wall. It results in initially, in thickening of the artery wall and eventually, in plaque buildup that can cause a heart attack or a stroke.
Another well known example of a harmful thing that can cause excessive oxidation and contribute to damage of the arteries and cardiovascular events, is smoking cigarettes. It’s well known that cigarettes are bad for the heart, and are bad for you in general. It is because smoking causes excessive chemical damage. Excessive oxidation.
And indeed, there can be other types of toxins, and other related causes that are not well known (which I will not cover just yet). I’ll give you an opportunity to learn about that later on. However, this one is one of the most important ones for most Westerners–polyunsaturated fatty acids or Vegetable oil.
Oxidation From Vegetable Oil (PUFAs)
Vegetable oil has polyunsaturated fatty acids, or PUFA’s for short. And this is perhaps the most important culprit of oxidation to become aware of. Limiting polyunsaturated fatty acids will help you increase the chances of avoiding all kinds of diseases, chronic diseases, degenerative diseases of the body and the mind.
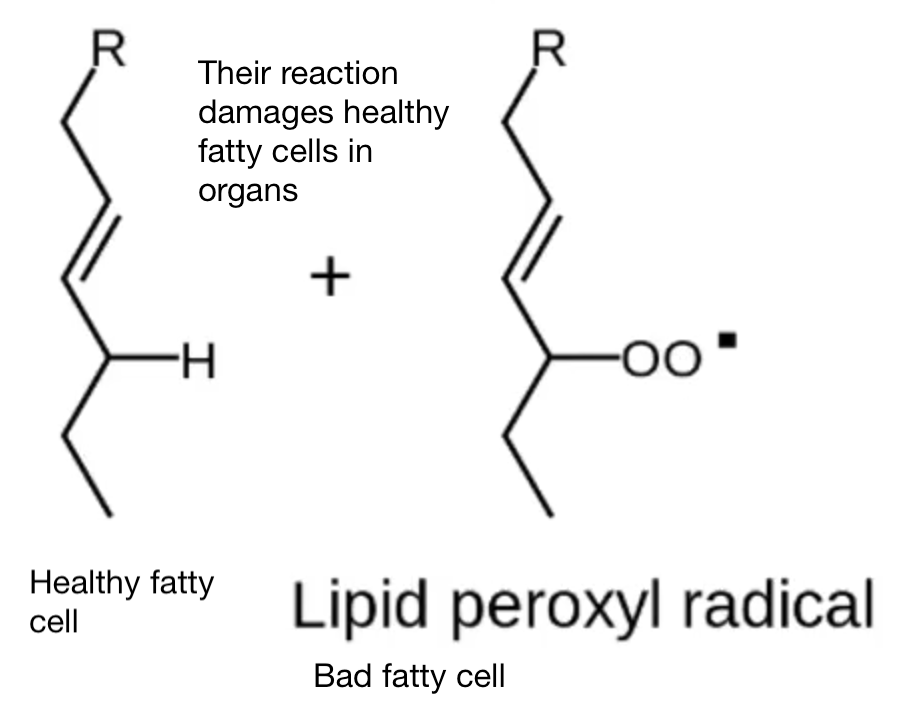
So this here is a representation of an unsaturated lipid–a fat in our body (upper-left). The structure of this lipid makes it very volatile and susceptible to reacting with this type of free, radical (*OH), and other free radicals as well. The *OH on the diagram is a hydroxyl radical, and this dot there represents an unpaired electron, a loose electron, and it easily interacts with the hydrogen on the lipid molecule. And part of the reaction, water is formed, but it results in what is a lipid radical.

Now, this unstable hydroxyl radical turns the unsaturated lipid into a lipid radical (upper right).
What’s the problem with that? Well, there are a lot of lipids in the human body and if we consume too much polyunsaturated fatty acids, this can start a chain reaction where, because of interaction with oxygen (O2), a lipid peroxide radical further becomes unstable. And it starts interacting with other unsaturated lipids, causing disease.
Oxidation Affects Organs Rich in Fatty Cells
The brain has a lot of lipids in it, and this oxidative damage can contribute to Alzheimer’s disease. This is a cross-section of a healthy brain from healthy individual and a brain from an Alzheimer’s patient, someone with advance Alzheimer’s disease. And you can see it’s a lot smaller than the healthy brain. Why? Largely because of this type of oxidative damage.

This can happen elsewhere as well. There are lipids also in the lining of the arteries. And it can damage the lining of the arteries as well. And so, the antioxidant defense systems, neutralize harmful molecules, and it consists of, or they consist of well known vitamins and minerals, and some well known molecules.







